What Does a Hip Labral Tear Feel Like?
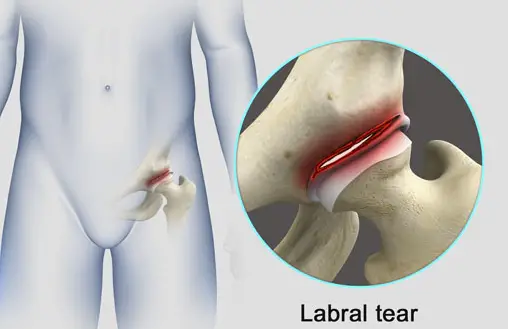
Hip labral tear is a medical state with a composition of the ring of fibrocartilage and dense connective tissue that takes the place on the exterior rim of the socket of patient’s hip joint.
Hip labral tear is considered as a driver of the hip pain and in the recent years, among the orthopedics, hip labral tear became a hot topic in the field of orthopedics. To understand the dynamics of the hip labral tear, we should focus on the labrum. The function of the labrum ( which is the ridge of cartilage) is to operate like a drinking cup for assisting people to grasp their hip joint closely and conjointly.
Within the general population, all people may develop hip labral tear especially individuals with structural abnormalities including osteoarthritis, over body weight, abnormal anatomic shape, and alignment etc… However, people in the field of sports professional are more exposed to hip labral tear.
You may find the kind of sports that athletes carry the risk of developing hip labral tear:
- American football.
- Soccer.
- Balley.
- Golfing.
- Ice hockey.
- Artistic ice skating
Opinion leaders of orthopedics state that, the hip labral tear is a mechanically induced pathology and the majority of them think that this is due to an enormous pressure at the hip joint. This is why certain sports may have a potential cause of hip labral tear. It is being clinically observed that the part of the athletes in mentioned sports is likely to develop a hip labral tear.
With the help of advanced research and development in diagnosing techniques in of orthopedics, the awareness and medical knowledge of hip labral tear have dramatically increased.
When orthopedic surgeons take the patient history, they clinically observe that the major symptoms of hip labral tear include hip pain or a catching sensation of people’s hip joint.
In addition to that, with the employment of an arthroscopy in the cases of the hip labral tear, it is very convenient to visualize the hip joint and analyze the hip injuries accordingly.
In theory, orthopedic surgeons can visualize the hip joint to make a proper diagnosis in hip labral tear. However, it should be underlined that the diagnosis of hip labral tear is relatively a new area in orthopedics. And clinically it is very often underestimated where physical findings of the hip labral tear are usually confusing the physicians and besides hip labral tear imaging studies are generally not specific. Thus diagnosing of hip labral tear is still a major challenge.
The clinical observation and experience of hip labral tear indicate that every year there is a growing number of hip labral tear surgery. Within the context of hip labral surgery, orthopedic surgeons can get rid off loose fragments within the hip joint and trim. It is also clinically possible to repair the hip labral tear with the use of arthroscopic techniques in clinical practice.
Contents
Hip Labral Tear Symptoms
Hip labral tear is underestimated due to its nature. Because many people with a hip labral tear are asymptomatic. Thus diagnosing of hip labral tear may be challenging for an orthopedic surgeon.
Symptoms of the hip labral tear are:
- Groin pain
- Restricted mobility of the hip joint, in other words experiencing stiffness or inflexibility
- Clicking sensation of the hip joint
- Locking sensation of the hip joint
- Catching sensation of the hip joint
The clinical presentation of hip labral tear is very contradictory, but the most common indicator is a sharp groin pain following a traumatic incident.
Pain is the most specific sign or symptom of the hip labral tear. However, it is important to remember that the pain itself may not the only indicator of the hip labral tear. Even clinicians observe a tear in the hip labrum on MRI; this cannot directly link with a hip labral tear.
There is needed to make a differential diagnosis of the hip labral tear, remembering that it has very much alike symptoms including:
- Sports hernia
- Snapping Hip
- Groin strain
- Other athletic injuries of the hip joint
People with hip labral tear may experience pain in the hip front and back together with groin pain. They may also suffer from a pain down the leg and a clicking when they rotate their leg across their body.
Patient feedback from the major orthopedic clinics reflect that when people with hip labral tear engage themselves in a certain physical activity like sports, cycling at the beginning everything is fine, but after a certain time, they have to quit because of the pain.
Orthopedic surgeons may require specific tests to determine the whether the pain is the cause of hip labral tear. In many cases of the hip labral tear, the X-rays looks normal. Depending on the clinical experience MRI test results may ease the diagnosis of hip labral tear when analyzing the labrum. However this not true for all. Although diagnosing hip labral tear is a challenging issue, with the proper use of hip arthroscopy, a hip labral tear can be both diagnosed and treated. The procedure takes almost 35 minutes. When physicians struggle with making a proper diagnosis in the existence of joint symptoms, MR imaging, and physical examination, hip arthroscopy is a frequently used technique performed as a day case operation. As a summary, to make a proper diagnosis hip arthroscopy, MRI, physical examination and clinical evaluation should together be considered.
Hip Labral Tear Treatments
Treatment of hip labral tear can be classified into 2 sub-categories:
1- Hip Arthroscopy
Hip arthroscopy is frequently preferred by orthopedic surgeons if the patient’s symptoms continue for more than a month. It is a surgical procedure for both diagnosing and treating hip labral tear. The orthopedic surgeon inserts arthroscope into the patient’s joint space through a small incision in the skin. A tiny camera projects the joint visual into the video screen with the proper lighting. As the orthopedic surgeon analyze the joint through small incisions he/she performs the arthroscopic surgery. Orthopedic surgeon evaluates the tear, and then he/she decides to cut or remove the torn piece of the labrum, or he/she may decide to repair the torn cartilage with a suturing procedure. It totally depends on the arthroscopic findings and the clinical evaluation of the orthopedic surgeon.
2- No surgery options
a) Medications
- Pain prescriptions
Mostly NSAIDs (Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are among the most widely used medications in the US, NSAIDs are very useful in controlling the hip labral tear related pain, and reducing the inflammation. The most common NSAIDs that are used to manage hip labral tear pain are:
Tylenol: we remind you that acetaminophen (Paracetamol; Tylenol) belongs to a class of drugs called analgesics (pain relievers) and antipyretics (fever reducers)
- Aleve
- Advil
- Motrin
- Nuprin
Corticosteroid injections
The clinical objective of the use of corticosteroid injections in hip labral tear is to reduce pain and joint inflammation. Corticosteroid injections. X-Ray results guide the use of corticosteroid injections.
b) Physical Therapy
With the guidance of a physical therapist, a patient with a hip labral tear can make regular exercises that will utilize hip strength and stability together with a hip range of motion. Physical therapists generally analyze the movements of the patients with a hip labral tear to check which movements put stress on their hip joint. The consequence of this observation will lead physical therapists to prevent the patients from such movements.
It is important to remember that, hip labral tear treatment options depends on the severity of the hip labral tear symptoms. Orthopedic surgeons will decide the optimum treatment alternative according to the physical presentation and findings of the patient.
What Does a Hip Labral Tear Feel Like? Last Update: 27/4/2017


Pingback: The Causes of Right Side above The Hip - Body Pain Tips
I see you don’t monetize your page, don’t waste your traffic, you can earn extra bucks every month because you’ve got high quality content.
If you want to know how to make extra money, search for:
best adsense alternative Wrastain’s tools
Pingback: Hip Labral Tear Symptoms in The Lower Back - Body Pain Tips
Pingback: 12 Worst Causes of Hip Bone Pain - Body Pain Tips
Pingback: Hip Joint Pain after Running: Causes and What To Do - Body Pain Tips